Baking of Rocks Surrounding an Igneous Intrusion Is Called
Hereof what are intrusive igneous bodies called. Xenoliths may be virtually unaffected and the original rock type and easily identifiable or reaction with the magma may take place to the extent that only an indistinct patch remains.
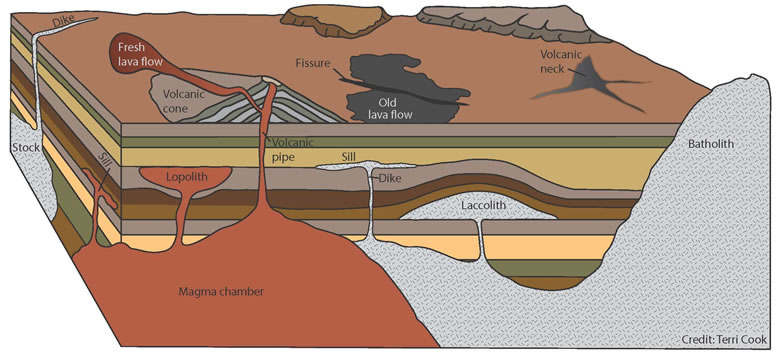
Igneous And Volcanic Rock Features
Examples of intrusive igneous.
. 2 Contact Metamorphism is the result of baking the surrounding country rocks by an igneous intrusion. Similarly a fine-grained mafic igneous rock is not only a basalt it is an extrusive. We call this metamorphic halo the baked zone and they can range in thickness from microscopic to 10s of meters when surrounding huge granitic intrusives.
The temperature in the Earth goes up with depth. Click to see full answer. This causes a baking of the neighboring rock called contact metamorphism.
Concordant or Discordant 8. Obviously when and igneous body some 1200 degrees C intrudes into unsuspecting host rock the contact zone heats up considerably. It does so in a few different ways including filling and widening existing cracks melting the surrounding rock called country rock 1 pushing the rock aside where it is somewhat.
Most foliation is caused by the preferred orientation of phylosilicates and glassy igneous rocks. Igneous rocks are called intrusive when they cool and solidify beneath the surface. Intrusive igneous rocks cool from magma slowly and have crystals that are easily seen with the naked eye.
True Indicate the typical sequence of formation for sedimentary rock landscapes beginning with the first event at the top and the last event at the bottom. The rocks closest to the contact with the intrusion are heated to the highest temperatures so the metamorphic grade is highest there and diminishes with increasing distance away from the contact. A type of metamorphism associated with the baking effects of an igneous intrusion is called.
The metamorphic aureole surrounding an igneous body may be only 2 centimeters wide adjacent to a small dike or it may be 2 kilometers wide at the contact with a large slow-cooling granite pluton. The term chill margin is also loosely applied to pillow basalt. On the other hand.
Obviously when and igneous body some 1200 degrees C intrudes into unsuspecting host rock the contact zone heats up considerably. 35 Intrusive Igneous Bodies In most cases a body of hot magma is less dense than the rock surrounding it so it has a tendency to move very slowly up toward the surface. Regional Regional Occur to a large volumearea of Earths crust Associated with orogenesis ie.
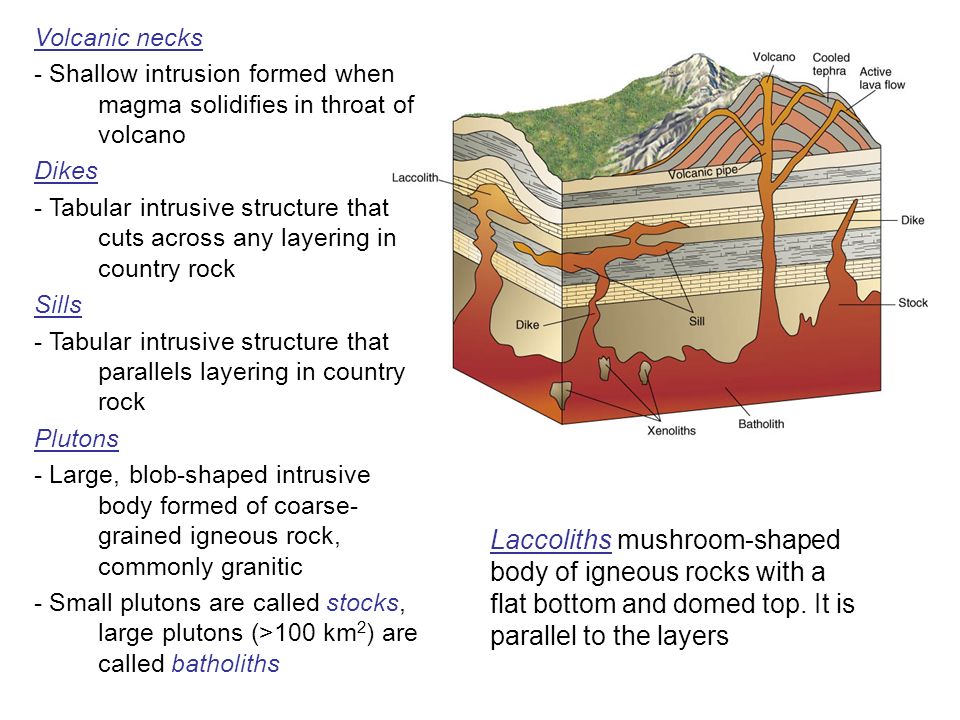
Intrusive rocks form plutons and so are also called plutonic. If an igneous body is parallel to or occur along bedding planes of country rocks. An igneous dike will bake the surrounding rock indicating that the dike is younger than the surrounding rock.
If it cuts across the bedding planes of surrounding rocks it is called discordant. Prolonged heat doesnt always melt the country rock but it does mobilize the elements and allow new minerals to form and grow that. Contact metamorphism A hard non-foliated rock produced by contact metamorphism is called.
The formation of mountain 造山運動 Building of mountains Not just along a fault as is the case with cataclastic metamorphism nor only adjacent to an igneous intrusion as happens with contact metamorphism. Extrusives only heat the rock below them and may not cause much. Its forms is called concordant.
An igneous dike will bake the surrounding rock indicating that the dike is older than the surrounding rock. Both intrusive and extrusive rocks may contain natural fractures from contraction while cooling and may have carried non-igneous rocks with them called xenoliths. Sediments and volcanic units are usually deposited in flat-lying layers inclusions rocks may incorporate older pieces of rock contact effects a baked zone forms next to a dike during intrusion Which chapter of geologic history is the earliest and represents 90 of.
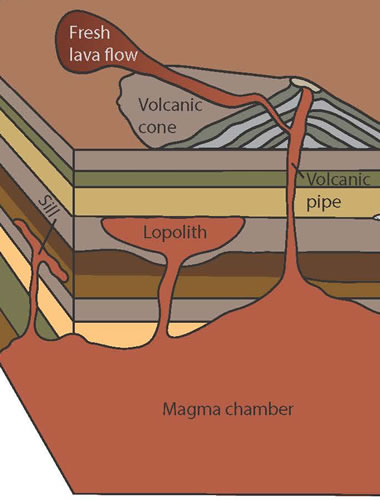
When a mass of magma punctures the overlying layers of rocks fragments of the country rock often become detached and surrounded by the magma these are called xenoliths Fig. Contact metamorphic rocks are formed when a hot igneous mass of magma forces its way through the earths crust literally baking the rock surrounding it. The temperature in the Earth goes up with depth.
Contact metamorphosed rocks may be bleached out looking and non-descript. Near the surface in ordinary crust the temperature rises some 30 degrees per kilometer. To develop regional metamorphism one of the following.
The intrusion of large bodies of granitebatholithsis usually part of the origin of a mountain range. If the pluton is large it may be called a batholith or a stock. Intrusive rocks may alter the rocks above and below them by metamorphosing baking the rock near the intrusion.
A body of intrusive igneous rock which crystallizes from magma cooling underneath the surface of the Earth is called a pluton. During this time they bake a zone or aureole of contact metamorphism in the country rock. Deep magma bodies cool very slowly and turn into coarse-grained plutonic rocks like granite and gabbro.
Aureole is a ring around an igneous intrusion. Sills produce baking effects on rocks on both sides molten lava. Changescan take place resulting in a metamorphic aureole extending into the surrounding rock.
This causes a baking of the neighboring rock called contact metamorphism. True Match the geologic term related to lateral changes in rock type with its meaning in the list shown. The zone of contact metamorphism surrounding an igneous intrusion is called the metamorphic aureole.
Near the surface in ordinary crust the temperature rises some 30 degrees per kilometer.

Geological Society Igneous Intrusions

Chapter 4 Intrusives Ppt Video Online Download

What Happens With An Igneous And Sedimentary Rock When They Come In Contact With Magma Quora
No comments for "Baking of Rocks Surrounding an Igneous Intrusion Is Called"
Post a Comment